Clinical Utility of High- Versus Low-Density EEG Source Imaging in Presurgical Evaluation: Impact on Decision Making
Abstract number :
1.153
Submission category :
3. Neurophysiology / 3C. Other Clinical EEG
Year :
2018
Submission ID :
498559
Source :
www.aesnet.org
Presentation date :
12/1/2018 6:00:00 PM
Published date :
Nov 5, 2018, 18:00 PM
Authors :
Mette T. Foged, Copenhagen University Hospital, Rigshospitalet; Terje Martens, Copenhagen University Hospital, Rigshospitalet; Nizar Hamrouni, Copenhagen University Hospital, Rigshospitalet; Lars H. Pinborg, Copenhagen University Hospital; Olaf B. Paulson
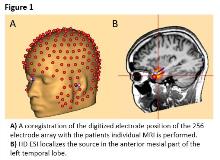
Rationale: To investigate the diagnostic added value of low-density (LD) and high-density (HD) EEG source imaging (ESI) in presurgical evaluation of patients with drug-resistant focal epilepsy. Previous clinical studies on EEG source imaging addressed the accuracy, but little is known about the clinical utility, defined as the added diagnostic value. Methods: Seventy-one patients undergoing epilepsy surgery evaluation in Denmark between 2015 and 2018 were included. LD ESI was based on long-term video-EEG recordings with standard 25 electrodes, and age-matched template head model. HD ESI was done using 90 minutes recordings with 256 electrodes array, digitized electrode positions and realistic head model using the patients´ individual MRI, figure 1. The multidisciplinary team made decisions in three steps: (1) based on all data except ESI; (2) adding LD ESI to the dataset; (3) adding HD ESI to the dataset. Changes in decision on patient-management options (stop / implantation of intracranial electrodes / alterations in implantation plan/ operation with perioperative electrocorticography/ operation/ extension of resection area) based on LD ESI and HD ESI were noted in the database. Results: Patient-management has changed as shown in Table 1. Based on LD ESI the decision was changed in 14/71 patients (20 %) and based on HD ESI in 19/71 patients (27 %). This difference was significant (p<0.001). Conclusions: ESI using HD array has significantly higher clinical utility than ESI using LD EEG data, providing significantly (p<0.001) more, non-redundant information for the presurgical evaluation. Funding: Lundbeck FoundationLennart Grams Mindefond, Danish Epilepsy Society
.tmb-.jpg?Culture=en&sfvrsn=1762cd14_0)