EARLY SEIZURE DETECTION BY NONLINEAR ANALYSIS OF EEG RECORDED SIMULTANEOUSLY FROM SCALP AND DEPTH ELECTRODES
Abstract number :
1.064
Submission category :
Year :
2004
Submission ID :
4165
Source :
www.aesnet.org
Presentation date :
12/2/2004 12:00:00 AM
Published date :
Dec 1, 2004, 06:00 AM
Authors :
1Piotr W. Olejniczak, 2Slawomir T. Kwasik, 2Magdalena Musielak, 1Michael E. Carey, 1Bruce J. Fisch, and 1Grant Butterbaugh
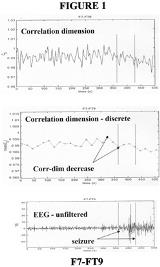
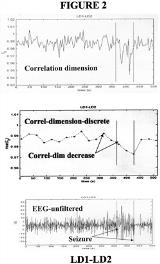
Early seizure detection is one of the fundamental problems in modern epileptology. It allows for timely intervention including pharmacotherapy, electrical stimulation and avoiding injury. It may also permit better localization in the workup for epilepsy surgery. Two complex partial seizures recorded simultaneously from intracranial and scalp electrodes in an awake patient undergoing evaluation for left temporal lobectomy were analyzed. The temporal evolution of the correlation dimension was computed using methods of nonlinear analysis. Decrease in the correlation dimension was observed for 20 seconds prior to the recognizable seizure onset in the F7-FT9 scalp lead (Figure 1) as well as in the left hippocampal LD1-LD2 lead (Figure 2). The same pattern was observed in two separate seizures. If confirmed by similar findings in other patients, the method of correlation dimension analysis may provide means of early seizure detection using either intracranial or scalp electrodes.[figure1][figure2]