PORPHYROGENICITY AND HEPATIC CYTOCHROME INDUCTION WITH NEW AEDS: LEVETIRACETAM, OXCARBAZEPINE AND ZONISAMIDE
Abstract number :
1.373
Submission category :
Year :
2004
Submission ID :
4401
Source :
www.aesnet.org
Presentation date :
12/2/2004 12:00:00 AM
Published date :
Dec 1, 2004, 06:00 AM
Authors :
Jan Krijt, and Gregory L. Krauss
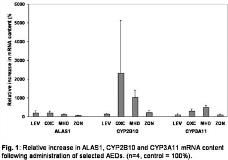
Most of the older antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) are strong inducers of hepatic 5-aminolevulinate synthase ([italic]Alas1[/italic]), the rate-limiting enzyme of hepatic porphyrin biosynthesis, and of hepatic cytochromes P450, which account for a significant part of total hepatic heme. Treatment of seizures in patients with acute porphyrias presents a difficult problem, since induction of these enzymes by many AEDs can lead to a porphyric attack. Induction of CYP450 and Alas1 are also important markers of AEDs[apos] capacities to be involved in drug interactions or to induce alterations in hepatic metabolism. We investigated whether the new generation AEDs, levetiracetam (LEV), oxcarbazepine (OXC) and zonisamide (ZON) alter the expression of selected cytochrome P450 mRNAs and ALAS1 mRNA in mouse liver. Male C57BL/6N mice were administered LEV (500 mg/kg ip.), OXC (150 mg/kg po.), MHD (150 mg/kg po.) or ZON (50 mg/kg po.) for 8 days. Expression of [italic]Alas1[/italic], [italic]Cyp2b10[/italic] (phenobarbital-inducible), [italic]Cyp2e1[/italic] (ethanol-inducible) and [italic]Cyp3a11[/italic] (steroid hormone-inducible) was investigated using real-time PCR. Results were expressed as the relative ratio of target mRNA/[beta]-actin mRNA and compared by Mann-Whitney U-test. Porphyrin content was determined methanol-sulphuric acid extraction and spectrofluorometric quantification. None of the AEDs tested caused an increase in fecal or urinary porphyrin excretion. In addition, none of the AEDs caused a statistically significant increase of the relative ratio of ALAS1 mRNA /[beta]-actin mRNA (Figure 1). LEV and ZON displayed no effect on CYP2B10, CYP2E1 or CYP3A11 mRNA. Both OXC and MHD, however, increased CYP2B10 mRNA content, and, to a lesser extent, CYP3A11 mRNA content.[figure1] Administration of [italic]Alas1[/italic]-inducing drugs or cytochrome P450-inducing drugs to acute porphyria patients is strongly discouraged. Results presented in this study demonstrate that LEV, ZON and OXC do not induce ALAS1 mRNA and porphyrin synthesis. Moreover, LEV and ZON are not inducers of CYP450, which suggests that LEV and ZON may be safe for treating seizures in patients with porphyria. OXC and MHD elevated CYP2B10 and 3A11 mRNA, but they did not alter porphyrin metabolism. Since the induction of CYP2B10 mRNA suggests, at least in mice, a possible effect on hepatic heme biosynthesis, more data are needed to evaluate the safety of OXC in porphyria patients. (Supported by UCB Pharma)