DISCRETE POPULATIONS OF NESTIN EXPRESSING CELLS IN HUMAN EPILEPTIC HIPPOCAMPUS: IMPLICATIONS FOR CELL REPLACEMENT STRATEGIES
Abstract number :
D.05
Submission category :
Year :
2003
Submission ID :
3604
Source :
www.aesnet.org
Presentation date :
12/6/2003 12:00:00 AM
Published date :
Dec 1, 2003, 06:00 AM
Authors :
Alexander A. Sosunov, Xiaoping Wu, Peter D. Crino, Robert R. Goodman, Guy M. McKhann II Neurological Surgery, Columbia University, New York, NY; Neurology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA
Epilepsy surgical tissue is a valuable source of progenitor cells. Based on developmental neurobiology and [italic]in vitro[/italic] mammalian work, many nestin expressing cells in the CNS are stem or precursor cells for neurons and/or glial cells. However, human nestin+ cells have been immunophenotyped to a limited degree. We sought to characterize the antigenic and structural properties of nestin+ cells in human TLE tissue.
Immunohistochemical and electron microscopic (EM) investigation of nestin+ cells in human hippocampus from surgical patients with intractable TLE: 31 hippocampi were studied, 21 with hippocampal sclerosis (HS) and 10 without sclerosis, based on MRI and neuropathological criteria.
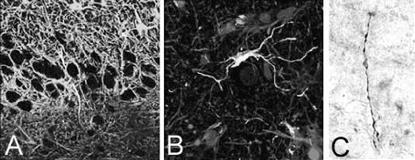
Four types of nestin+ cells were identified: 1) Radial glial cells, observed mainly in young patients, have characteristic structural features and are GFAP+, vimentin+ (Fig.1a), S100[beta]+ (mainly in nucleus), and glutamine synthatase- (GS). 2) Fibrous-like astrocytes have large, long processes and are usually found in [italic]str. lacunosum-moleculare[/italic] or near areas of sclerosis. These cells are strongly vimentin+ 3) Unusual nestin+ cells with small perikaryon and curved processes that are tightly apposed to neuronal cell bodies. These cells are located in hilus, CA3, and regions of CA1, in areas where reactive astrocytes are also found. Detected in 8 hippocampi (4 cases with HS, 4 without HS), these cells are GFAP-, GS-, CD68- (microglial marker), and vimentin+, S100[beta]+ (Fig. 1b), NG2+. 4) Bipolar cells found in the hilus (Fig. 1c) and surrounding white matter, often in contact with blood vessels. They are GFAP-, S100[beta]-, GS-, NG2-, vimentin+. By EM, the third and fourth cell types have features of undifferentiated cells: condensed nuclear chromatin and few cytoplasmic specialized organelles.
There are four populations of immunohistochemically and anatomically discrete nestin+ cells in human hippocampus from TLE patients. The neurogenic and gliogenic potential of each of these populations remains under investigation and will ultimately determine their usefulness in cell replacement strategies. Bipolar nestin+ cells may represent a white matter pool of neuronal/glial precursors, less differentiated than the multipotential neural progenitors isolated from adult human white matter with A2B5 surface antigen sorting (Nunes et al., Nat.Med. 9: 439-447, 2003).[figure1] A) radial glia cell: nestin+(red), vimentin+(blue), GFAP+(green); B)nestin+/S100[beta]+ (red) in perineurinal position in hilus. C) bipolar cell (peroxidase method)
[Supported by: Klingenstein Foundation, Parents Against Childhood Epilepsy, NIH R21 NS 42334]